3D Dental Scans vs. Traditional X-Rays: What’s the Difference?
by Dr. Labeeb
18 March 2025
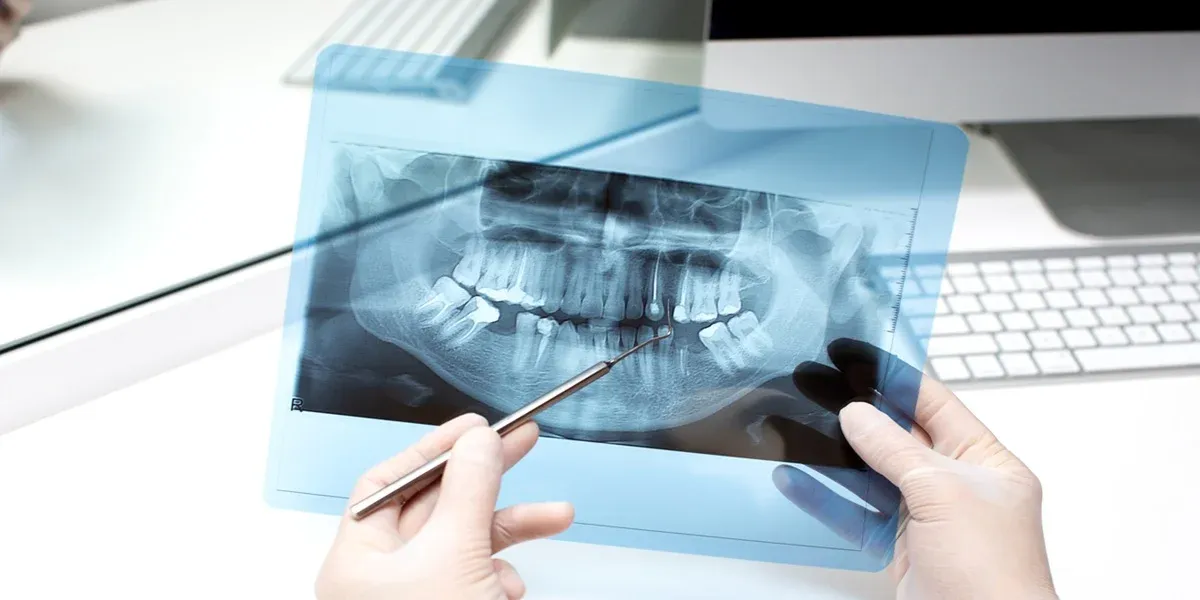
Dental imaging helps dentists diagnose problems, plan treatments, and monitor oral health over time. For decades, traditional X-rays have been the standard for capturing images of teeth, gums, and jawbones. However, advancements in technology have introduced 3D dental scans, which provide more detailed and accurate images.
Both methods have their place in dentistry, but they serve different purposes. Traditional X-rays are useful for routine exams, while 3D scans help in complex procedures like implants and oral surgery. Understanding how these technologies work, their benefits, and their differences can help patients feel more informed about their dental care.
How Traditional X-Rays Work
Traditional X-rays have been used in dentistry for years. They provide a basic view of the teeth and surrounding structures, helping dentists detect cavities, infections, and bone loss.
The Basics of 2D Dental X-Rays
Traditional dental X-rays use small amounts of radiation to create two-dimensional images of the mouth. These images show the structure of teeth and jawbones but lack depth. The most common types of dental X-rays include:
- Bitewing X-rays – Show the upper and lower back teeth to detect cavities and bone loss.
- Periapical X-rays – Capture the entire tooth, including the root and surrounding bone.
- Panoramic X-rays – Provide a broad image of the entire mouth, including the jaw and sinuses.
Dentists use these X-rays to identify decay, monitor bone health, and plan treatments like fillings and extractions.
Limitations of Traditional X-Rays
While 2D X-rays are helpful, they have limitations.
- They only show one angle of the tooth, meaning some issues can be hidden.
- Teeth that overlap can block cavities from being seen.
- They do not provide detailed images of nerves, soft tissues, or sinus cavities.
- Bone loss may not be fully visible in early stages.
Because of these limitations, dentists may need additional imaging for complex dental procedures.
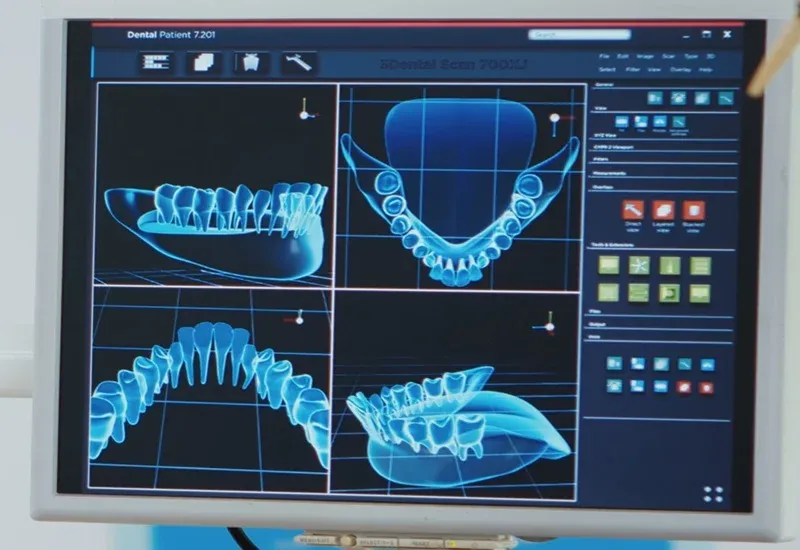
How 3D Dental Scans Work
3D dental scans use advanced imaging technology to provide a complete, three-dimensional view of a patient’s oral structures. These scans offer more accuracy and detail than traditional X-rays.
What Is a 3D Dental Scan?
A 3D dental scan, or Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scan, rotates around the head to capture multiple images. These images are then combined to create a 3D model of the teeth, jaw, nerves, and soft tissues.
Unlike 2D X-rays, CBCT scans allow dentists to see the mouth from different angles. This makes it easier to diagnose problems and plan treatments with precision.
Advantages of 3D Dental Scans
3D imaging provides a clearer, more complete picture of the mouth. Some key benefits include:
- Improved diagnosis – Dentists can detect infections, fractures, and bone loss that may not be visible on 2D X-rays.
- Better treatment planning – The detailed images help in procedures like implants, root canals, and jaw surgeries.
- Clearer views of nerves and sinuses – This helps avoid complications during surgery.
- Accurate bone measurements – Essential for planning dental implants and orthodontic treatments.
Because 3D scans capture more detail, they are preferred for cases where precision is critical.
When Are Traditional X-Rays Still Useful?
Even with advancements in 3D imaging, traditional X-rays remain a valuable tool in dentistry. They are quick, affordable, and effective for many common dental issues.
Routine Dental Check-Ups
Dentists use traditional X-rays during regular exams to check for cavities, gum disease, and early signs of decay. These X-rays help detect:
- Small cavities between teeth.
- Bone loss caused by gum disease.
- Hidden infections under the gums.
Bitewing and periapical X-rays are often part of standard check-ups and are useful for monitoring changes in oral health over time.
Situations Where 3D Imaging May Not Be Necessary
While 3D scans provide more detail, they are not needed for every patient. Traditional X-rays are still preferred in cases such as:
- Simple cavity detection.
- Routine monitoring of fillings or crowns.
- Checking wisdom teeth that are not causing problems.
Because traditional X-rays expose patients to less radiation and cost less, they remain the first choice for general dental care.
When Are 3D Dental Scans Necessary?
3D scans are essential for complex procedures that require a full view of the mouth, jaw, and nerves. They provide better accuracy for treatment planning and diagnosis.
Complex Dental Procedures
For treatments that involve bone structure, nerves, or detailed planning, 3D scans are the preferred choice. These include:
- Dental implants – Helps determine if there is enough bone to support an implant.
- Root canals – Provides a complete view of the root system to ensure proper treatment.
- Wisdom tooth extractions – Identifies the exact location of the tooth and its relation to nerves.
Because 3D scans capture all angles of the mouth, they help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Diagnosing Hidden Problems
Some dental issues are not visible with 2D X-rays. 3D imaging is useful for:
- Identifying impacted teeth – Helps locate teeth that haven’t fully emerged.
- Detecting cysts or tumors – Provides a clearer image of abnormal growths in the jaw.
- Assessing sinus-related dental pain – Determines if dental pain is caused by sinus issues.
When a dentist suspects a deeper problem, a 3D scan can provide the answers needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Comparing Radiation Exposure in Both Methods
One common concern with dental imaging is radiation exposure. While both 2D X-rays and 3D scans use radiation, the levels differ.
Traditional X-rays use low radiation doses, like what a person receives from natural background radiation in a day. 3D scans use higher doses, but they are still much lower than medical CT scans.
Dentists minimize radiation exposure by only using 3D scans when necessary. For routine care, traditional X-rays are preferred due to their lower radiation levels.
Cost Differences Between 3D Dental Scans and X-Rays
The cost of dental imaging varies depending on the type of scan and the dental office.
Affordability of Traditional X-Rays
Traditional X-rays are the most affordable option for routine dental care. Many insurance plans cover these X-rays as part of regular check-ups.
Because they are widely available and easy to use, traditional X-rays remain the most cost-effective option for general dentistry.
Why 3D Scans Cost More
3D dental scans require specialized equipment and additional processing. Although more expensive, 3D scans provide detailed images that can prevent complications during procedures. Some insurance plans cover them if they are medically necessary, but patients should check with their provider before scheduling a scan.
Conclusion
Both traditional X-rays and 3D dental scans are important tools in dentistry. Traditional X-rays are best for routine check-ups and diagnosing common dental issues, while 3D scans provide more detail for complex procedures.
For patients needing implants, root canals, or oral surgery, 3D scans help with accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Understanding the differences between these imaging methods allows patients to make informed decisions about their dental care. Those with concerns about cost or radiation exposure should discuss their options with their dentist to determine the best approach for their needs.
Contact your Dentist today at Studio city Dental, to learn more about ways to relieve painful gums.
Resource:
Share This:
Disclaimer
*This media/content or any other on this website does not prescribe, recommend, or prevent any treatment or procedure. Therefore, we highly recommend that you get the advice of a qualified dentist or other medical practitioners regarding your specific dental condition. *

